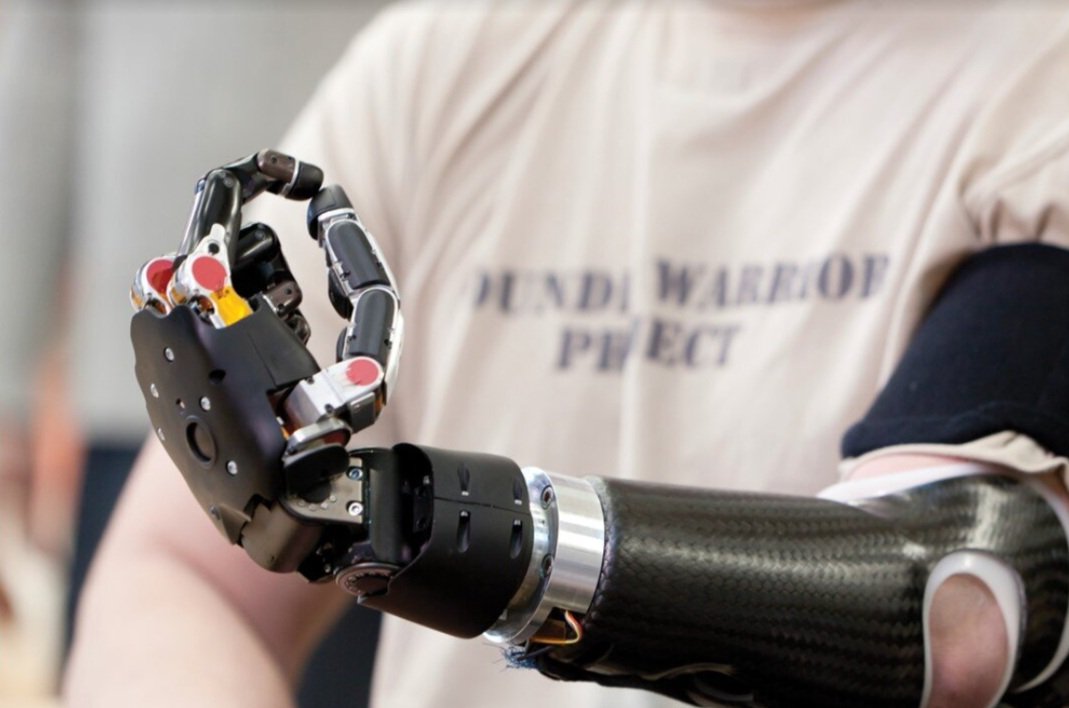
Electric Prostheses
Electric prostheses are artificial limbs that use the muscles of the residual limb to control the movement of the prosthetic limb. Electric prostheses are powered by a battery, and use several motors to make the joints in the device move.
Users can control the electric prosthesis in many ways:
Electric signals from muscles
Switches
Pressure sensors
There are several pros and cons that apply to all electric prostheses, no matter how they are controlled.
Pros:
Appropriate for people with different levels of upper limb loss and various levels of function, including people with above-elbow (transhumeral) and below-elbow (transradial) limb loss.
Can look more like a real arm than body-powered prostheses because they lack external cables and hardware.
Electric prostheses offer a strong grip force, often stronger than what body-powered prostheses can offer.
Cons:
Heavier than body-powered prostheses.
More expensive upfront and more costly to repair than body-powered prostheses.